1. Definition and Nature
Pixel Layers
- Nature: Bitmap layers based on pixels, raster images composed of pixel points
- Representation: Contain specific image content such as photos, paintings, or other pixel elements
- Storage Method: Memory usage related to resolution; higher resolution results in larger file size
Path Layers
- Nature: Vector-based mathematical paths composed of anchor points and Bézier curves
- Representation: Exist as outline lines in the Paths panel and do not directly display on the canvas
- Storage Method: Only records path coordinate information, does not occupy pixel memory, small file size
2. Core Feature Comparison
| Feature | Pixel Layers | Path Layers |
|---|---|---|
| Scaling Characteristics | Distorts and blurs when enlarged | Maintains clarity with infinite enlargement |
| Editing Method | Directly modifies pixels with brushes, erasers, etc. | Modifies curve shapes by adjusting anchor points and handles |
| Color Properties | Contains color information of pixels | No inherent color; requires stroking/filling to add color |
| Filter Support | Can directly apply all PS filter effects | Does not support filters; requires conversion to selection first |
| Selection Relationship | Can be converted to selection but process is irreversible | Can be converted to selection at any time while maintaining editability |
3. Main Uses
Suitable Scenarios for Pixel Layers
- Photo retouching and editing (e.g., portrait retouching, color adjustment)
- Pixel-level painting creation (directly drawing with brush tools)
- Compositing multi-layer images (overlay effects through blending modes)
- Adding text effects (text layers are essentially special pixel layers)
Suitable Scenarios for Path Layers
- Drawing precise graphics (e.g., logos, icons, and other vector elements)
- Creating complex selections (more flexible than marquee tools)
- Designing smooth curves (e.g., decorative lines in posters)
- Making custom shapes (can be saved as preset shapes for reuse)
4. Mutual Conversion Methods
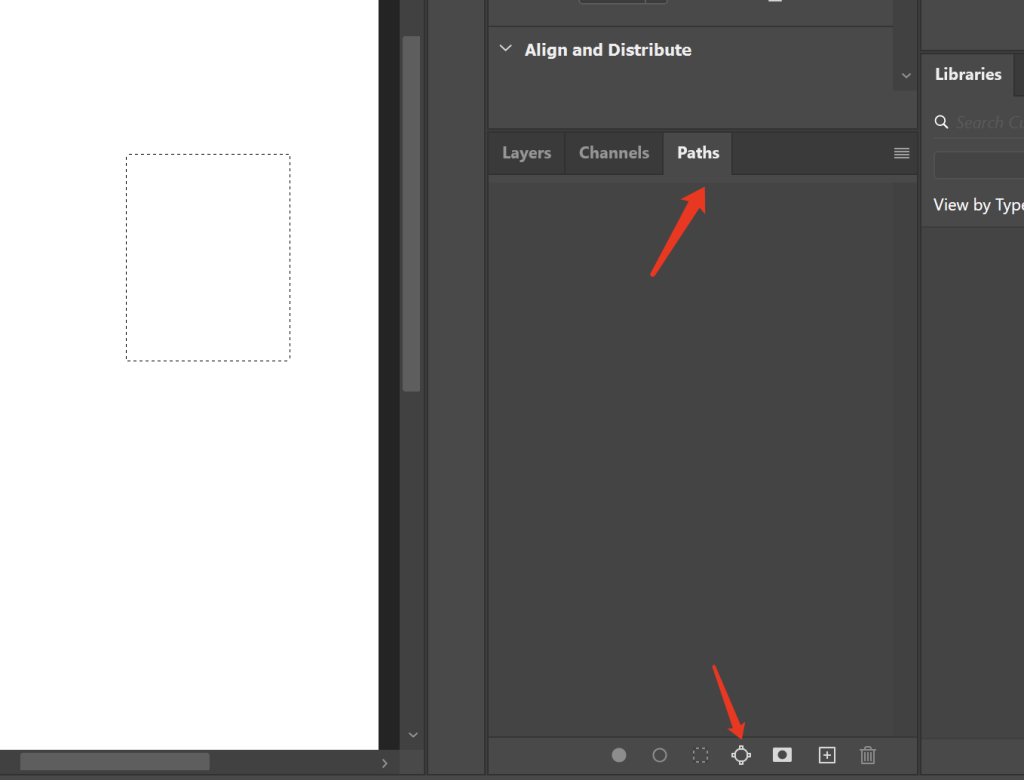
Converting Pixel Layers to Paths
- Create a selection using selection tools
- Convert via “Generate Work Path from Selection” in the Paths panel
- Further edit anchor points to optimize the path after conversion
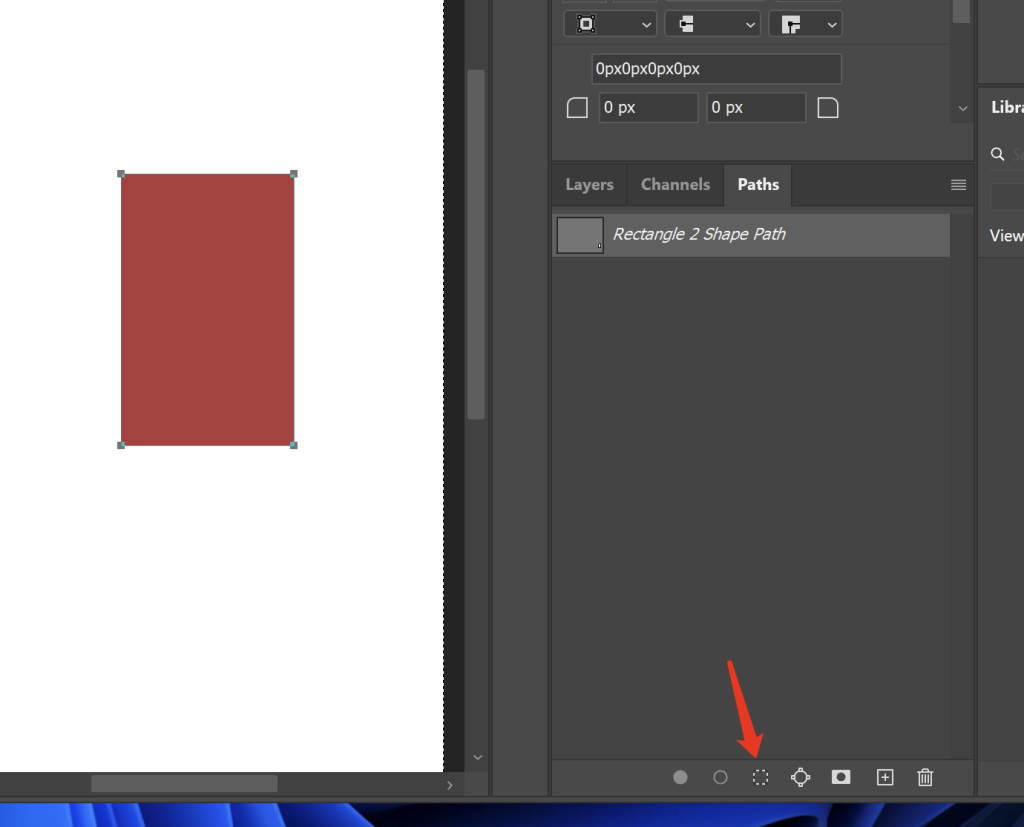
Converting Paths to Pixel Layers
- Select the path and click “Stroke Path” or “Fill Path” in the Paths panel
- Choose stroke/fill tool and properties
- The operation will generate pixel content on the current pixel layer
5. Advantages and Disadvantages Summary
Pixel Layers
- Advantages: Intuitively visible, diverse editing methods, supports all image effects
- Disadvantages: Quality loss when scaled, limited modification precision, high-resolution files consume more resources
Path Layers
- Advantages: Infinite scalability, precise editing, low resource consumption, reusable editing
- Disadvantages: No direct visual effect, requires conversion to apply filters, relatively complex operation
5. Practical Application Recommendations
- Logo/Icon Design: Prioritize path layers to ensure scaling clarity
- Photo Processing: Use pixel layers for pixel-level editing
- Complex Selections: First draw precise outlines with paths, then convert to selections for application to pixel layers
- Print Design: Use path layers for key elements to ensure output quality
- Web Design: Combine both – paths for UI elements and pixel layers for photo materials
Original link:https://www.ntutorial.com/143.html,Please indicate the source when reposting.

Comments2