1. Definition and Nature
Smart Objects
- Nature: Container objects that store raster or vector image data while preserving original image information
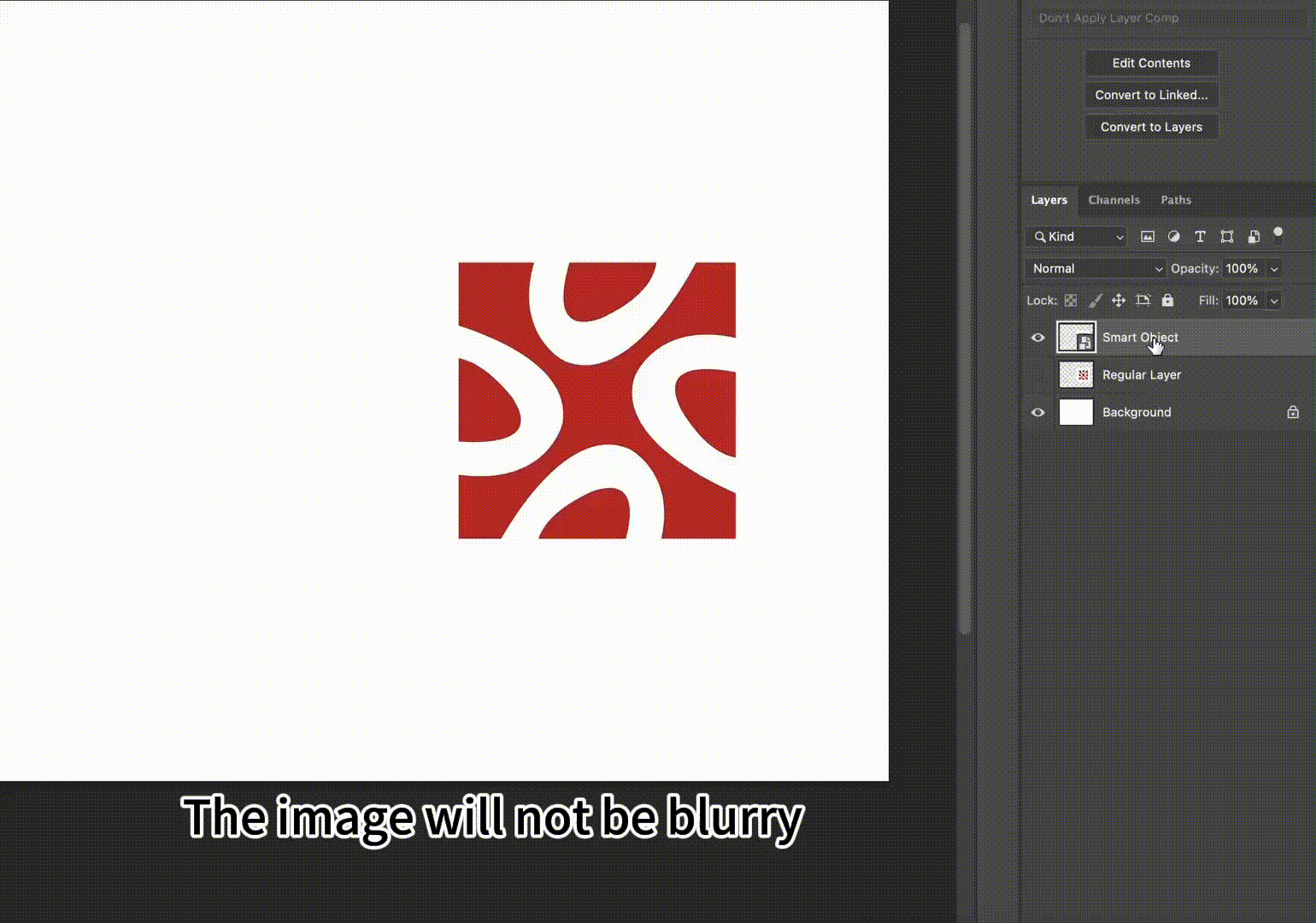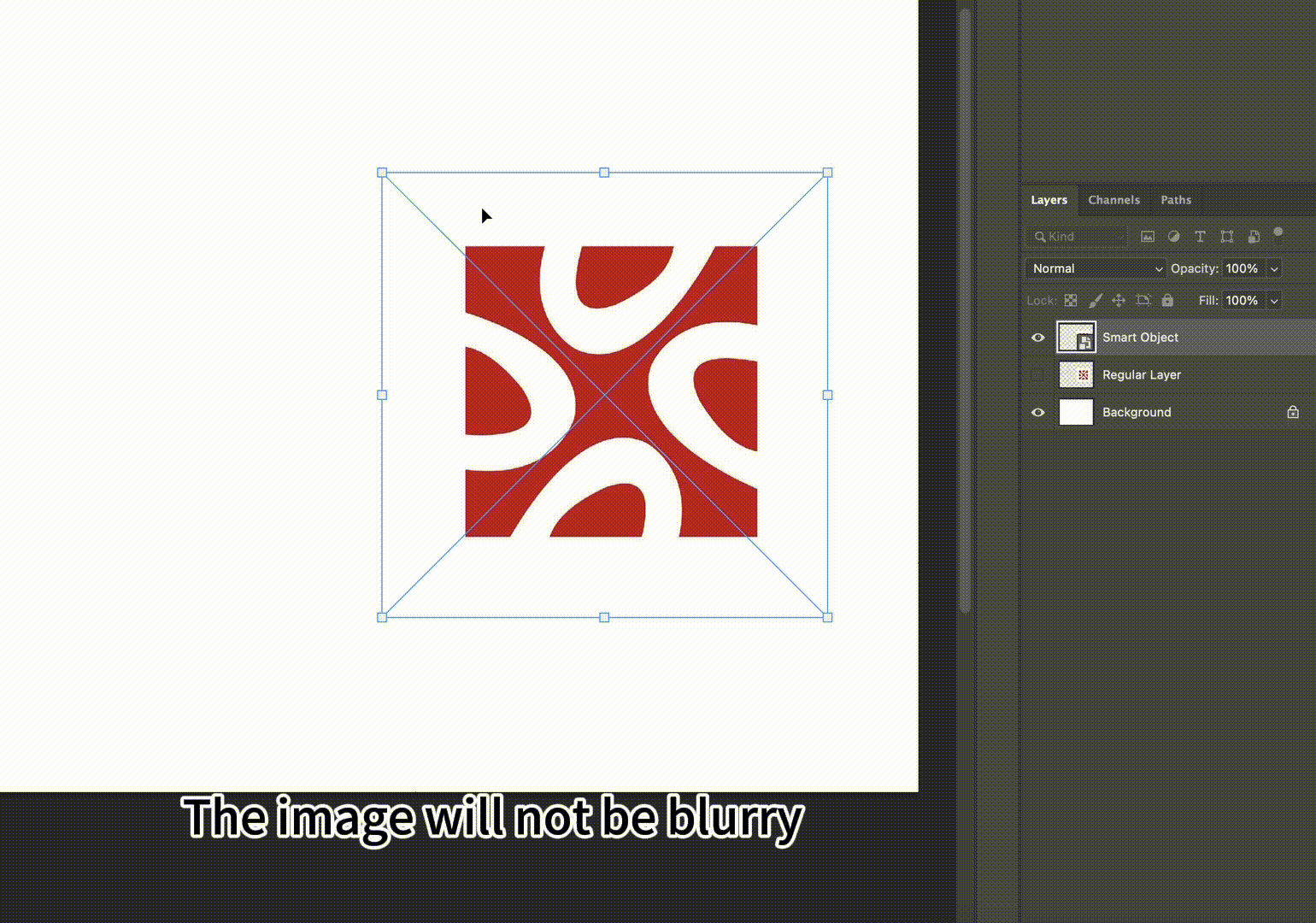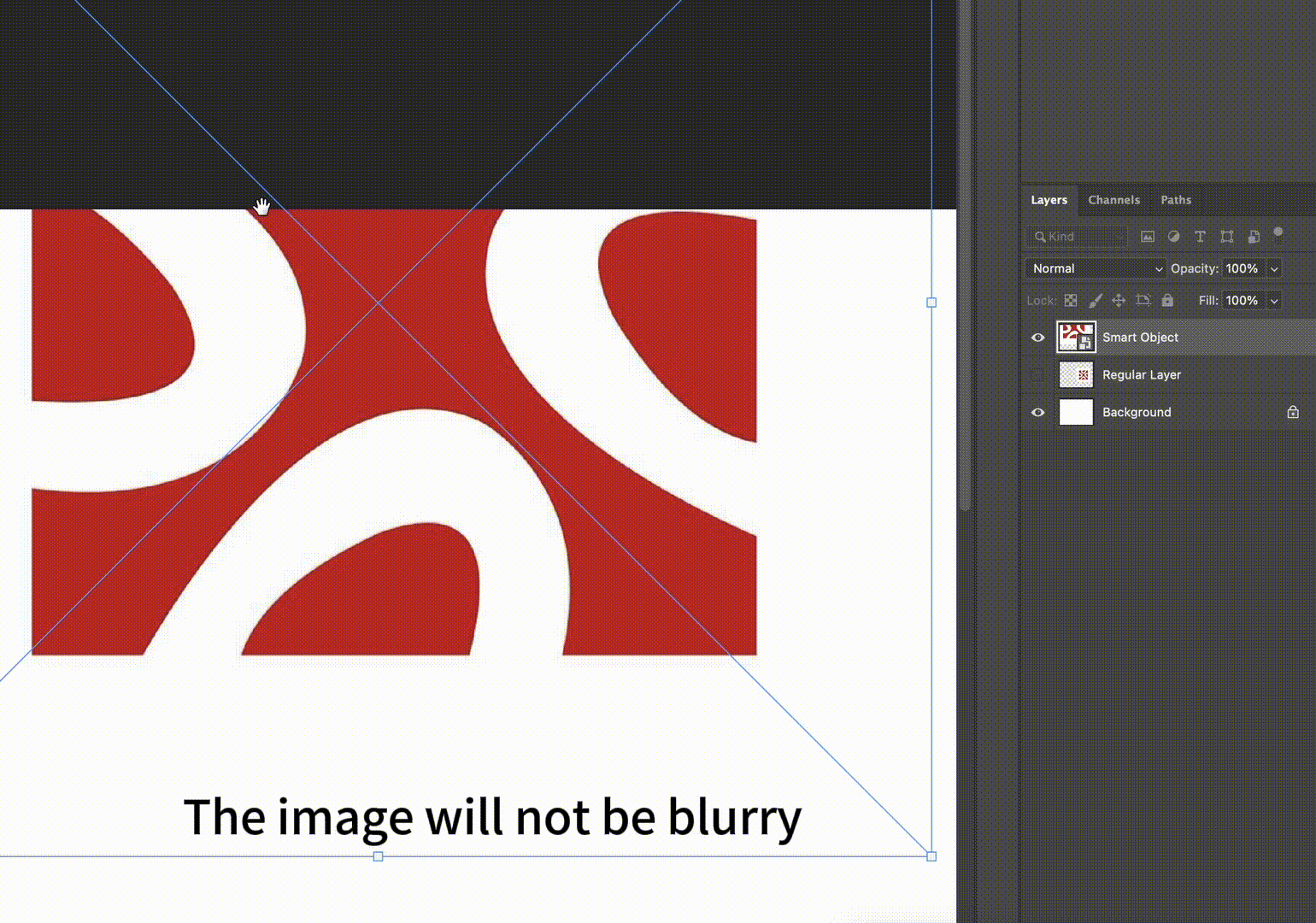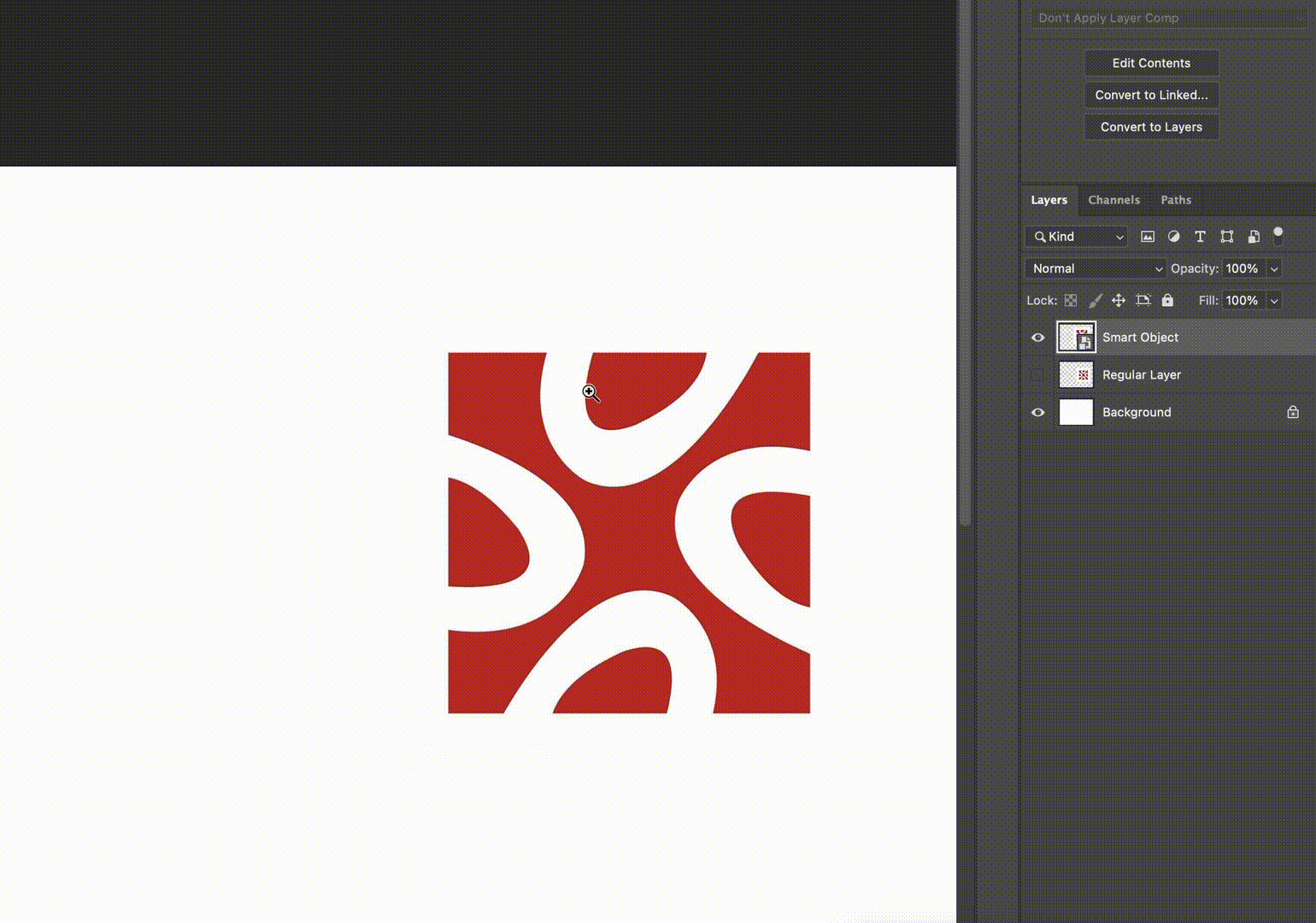
- Core Feature: Supports Non-destructive Editing, where all transformation operations do not directly modify pixels
- Data Storage: Embeds or links external image files, retaining original resolution and layer structure
Regular Layers
- Nature: Pixel-based editing layers composed directly of pixel points in a raster image
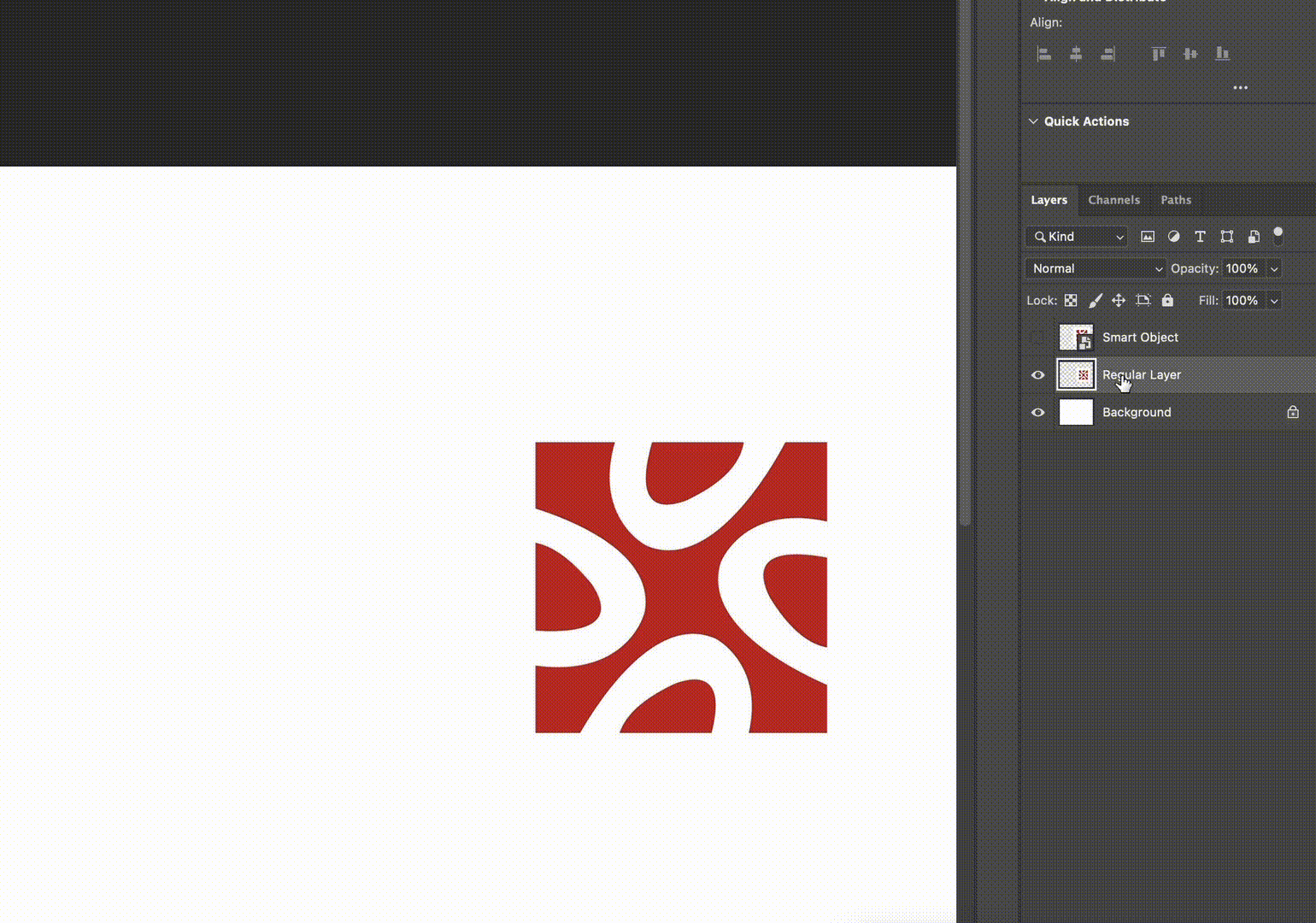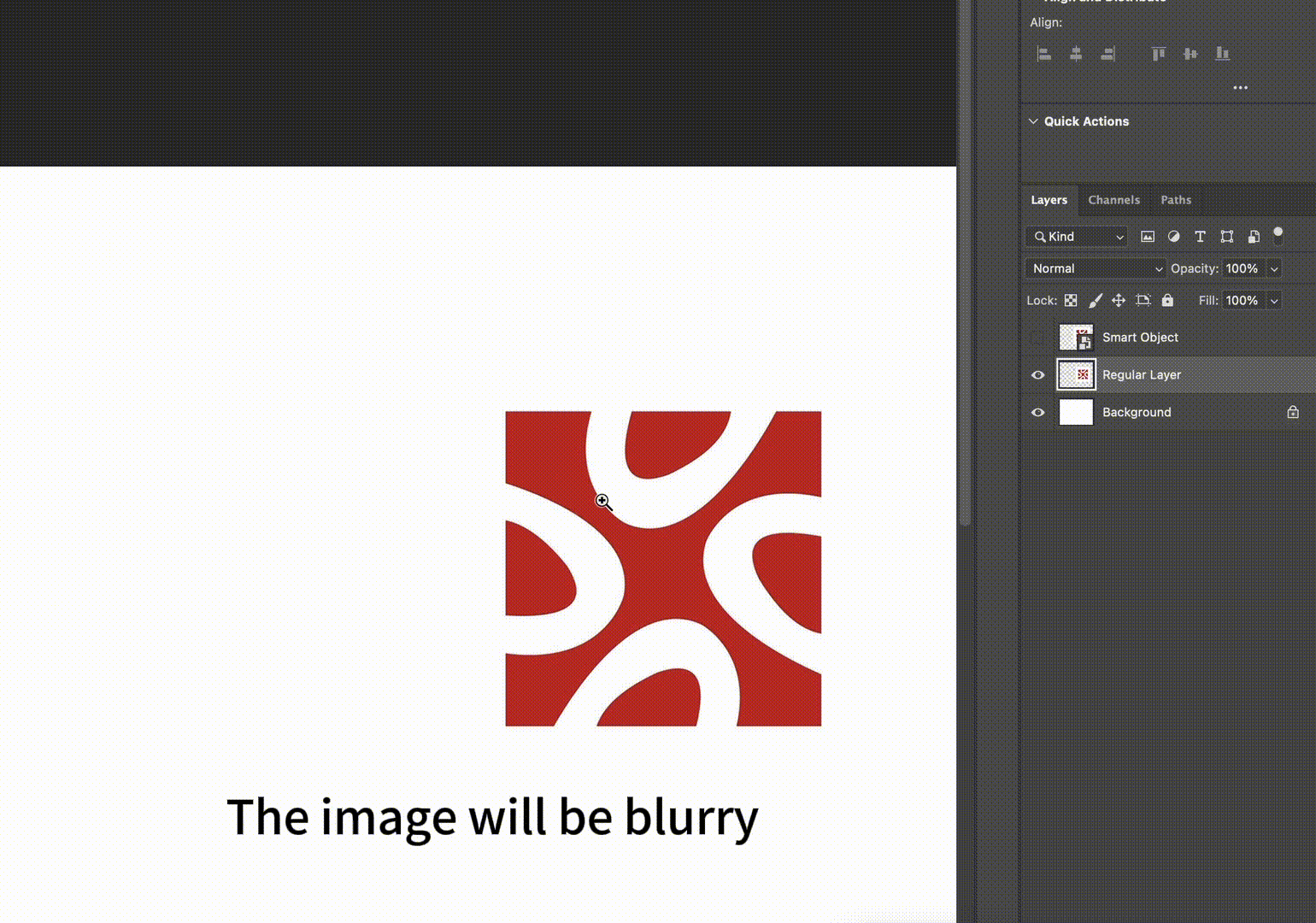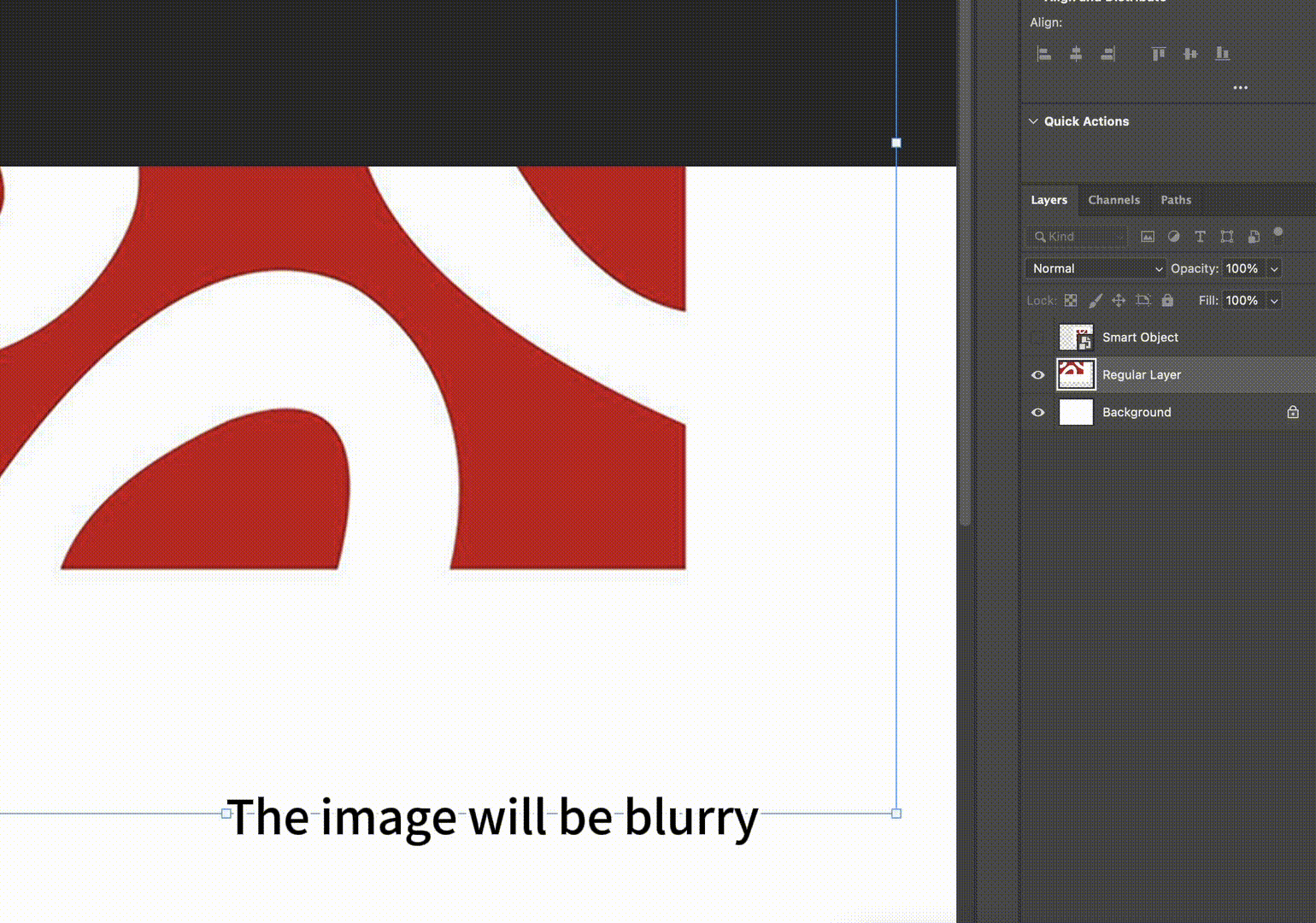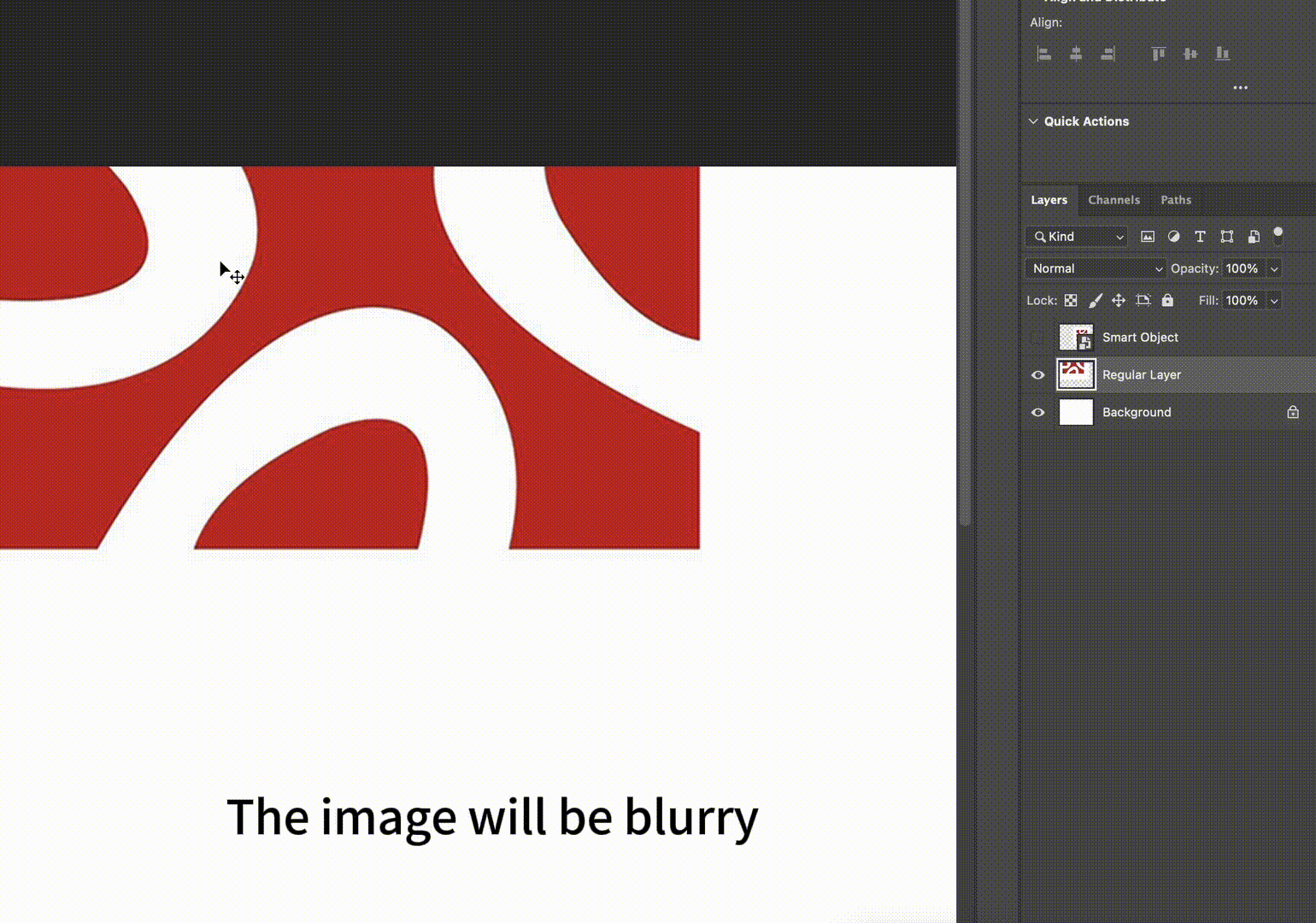
- Core Feature: Destructive Editing, where transformation and filter operations permanently alter pixel data
- Data Storage: Directly merges pixel information into the PSD file, making original state irrecoverable after modifications
2. Core Feature Comparison
| Feature | Smart Objects | Regular Layers |
|---|---|---|
| Scaling Performance | Unlimited non-destructive scaling while maintaining original image quality | Scaling beyond original size causes pixel blurring; cannot restore details after downscaling then upscaling |
| Filter Application | Filter effects exist as Smart Filters that can be edited or removed at any time | Filters directly modify pixels; changes require using history states or undo operations |
| Transformation Operations | All transformations (rotation/distortion/perspective) can be re-edited via the “Smart Objects” panel | Pixels permanently change after transformation; multiple transformations accumulate quality loss |
| External Linking | Can link external PSD/AI/RAW files, with automatic synchronization when source files are updated | Cannot link external files; requires manual copy-paste to update content |
| Editing Flexibility | Supports nested Smart Objects, preserving multi-layer editing structures | Cannot separate merged layers; editing hierarchy is single-level |
3. Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
Smart Objects
- Advantages:
- Preserves original image data, supporting unlimited non-destructive edits
- Smart Filters allow individual parameter adjustment or masking with reversible editing process
- Linked external files facilitate team collaboration and version management
- Ideal for complex design projects requiring multiple modifications
- Disadvantages:
- Increases PSD file size, especially when embedding multiple high-resolution images
- Some operations are restricted (e.g., direct pixel editing with brush tools)
- May require rasterization after applying filters for advanced pixel editing
- Higher computer configuration requirements; complex files may run slowly
Regular Layers
- Advantages:
- Smaller file size with faster operation speed
- Supports all pixel-level editing tools for direct and efficient operation
- Suitable for simple editing tasks and quick draft production
- Good compatibility, running smoothly on low-specification devices
- Disadvantages:
- Editing is irreversible; mistakes may require rework
- Multiple transformations cause image quality degradation
- Cannot directly reuse or update external file content
- Complex projects require numerous layers, making management difficult
4. Application Scenario Comparison
PS intelligent layer priority usage scenario
- Brand Design: Logo and brand elements need to maintain vector precision for multi-size output
- Photography Post-processing: Preserves original data after RAW format conversion for repeated parameter adjustments
- Template Creation: Design templates requiring batch updates (e.g., business card, poster templates)
- Team Collaboration: Maintains resource synchronization when multiple people edit the same project
- Print Design: Ensures optimal resolution across different image sizes
PS ordinary layer priority use scene
- Quick Image Retouching: Simple cropping, color adjustment, and filter application
- Pixel Art Creation: Direct pixel-level creation using brush tools
- Web Design Assets: Fixed-size icons and UI elements
- Low-specification Devices: Ensures smooth operation on computers with limited performance
- Final Output Layers: Merging visible layers for export or printing
5. Practical Operation Recommendations
Smart Objects Usage Tips
- Right-click layer > Convert to Smart Object for quick creation
- Alt+double-click Smart Object thumbnail to open original file for editing
- Smart Filter masks allow单独控制 filter application范围
- Use “Layer > Smart Objects > Replace Contents” to update linked files
- Nested Smart Objects should maintain clear hierarchy to avoid excessive complexity
Regular Layers Usage Tips
- Press Ctrl+J to duplicate layers before important edits to preserve original data
- Use Adjustment Layers instead of direct color adjustments for limited non-destructive editing
- Save duplicate files before merging visible layers
- Frequently use Ctrl+S to save to avoid rework from operation mistakes
- Use layer groups in complex projects to categorize and manage related content
6. Conversion and Compatibility
Converting Smart Objects to Regular Layers
- Operation Path: Right-click Smart Object layer > Rasterize Layer
- Consequences: Loses non-destructive editing capabilities; all Smart Filters become permanent effects
- Applicable Situations: Simplifying files before final output or requiring pixel-level precision editing
Converting Regular Layers to Smart Objects
- Operation Path: Right-click regular layer > Convert to Smart Object
- Notes: It is recommended to save layer state before conversion; original pixel editing history cannot be restored after conversion
- Best Practice: Important layers should be converted to Smart Objects immediately to preserve editing flexibility
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why do Smart Objects remain clear after scaling?
A: Smart Objects store original image data and recalculate pixel distribution during scaling rather than stretching existing pixels, thus maintaining clarity.
Q2: Do Smart Objects increase file size?
A: Yes, embedded Smart Objects retain complete original data. For large files, it is recommended to use “linking” rather than “embedding”.
Q3: How to achieve non-destructive editing with regular layers?
A: You can combine Adjustment Layers and Layer Masks to simulate some non-destructive effects, but with less flexibility than Smart Objects.
Q4: Do Smart Objects support all Photoshop features?
A: Some filters and tools require rasterization first, such as Liquify and certain pixelation filters.

Comments0